Combination therapies offer ways of targeting several mechanisms or pathways simultaneously and have become vitally important in the treatment of many cancer patients. Using syngeneic mouse models (described here), efficacy improvement is monitored compared to single treatment in terms of survival, tumour volume evolution and immune system modulation. MImAbs offers in vivo pharmacology for combination therapies that involve anti-PD1 or anti-CTLA4 treatments.
In practice, mice are subcutaneously injected with syngeneic tumour cells. When tumour volume reaches a predetermined size, the animals are subjected to intravenous injections of the antibodies (alone or in combination), and monitored for efficacy readouts. In the data presented, anti-PD1 and anti-CTLA4 were tested alone or in combination in C57Bl/6 mice injected with MC38 tumour cells.
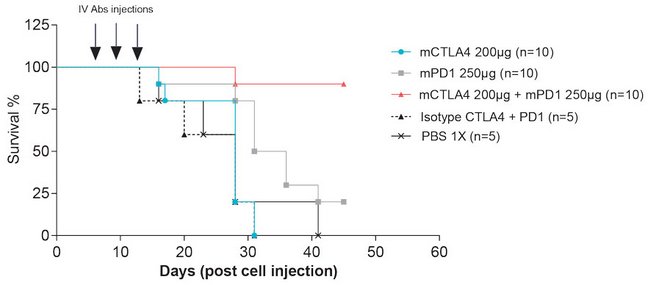
Survival
With the combination treatment: mouse survival is greatly improved (90% survival)
Tumour-free mice
The effect on survival correlates with tumour regression: up to 80% of tumour-free mice ~25 days after combination treatment.
Tumour volume
An intermediate effect is observed with anti-mPD1 alone and no obvious effect is observed with anti-CTLA4 alone.